An invisible, odorless, and hardly perceptible pollution, to which most of us contribute without being aware of it… Although it is considered more ecological because of its dematerialized aspect, digital technology is a source of pollution that is rapidly growing!
The digital sector’s average energy consumption is increasing by 4% per year, and more than 4 billion people around the world now use digital devices for personal and professional use.
Eminence examines the most energy-consuming digital uses and their impact on the environment. We will then recommend eco-responsible solutions that you can put in place from now on, both at your personal level and at your company’s.
I. What is the impact of digital on the environment?
According to The Shift Project, digital technology generated 4% of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2018. This rate is expected to reach 7% in 2025, due to a 9% annual increase in its use.
In order to better understand the importance of digital technology in our daily lives, let’s explore some concrete data and key figures:
- Digital technology generates 1.5 times more greenhouse gas emissions than air traffic.
- An e-mail sent has a carbon footprint of 4 grams and this rises to 11 grams for an e-mail with a 1 MB attachment. Its environmental weight can even correspond to the printing of 120 pages in case of a large attachment!
- According to WWF, 10 billion emails are sent every hour worldwide, which is the energy equivalent of 4,000 round trips from Paris to New York.
- 1 Google search is the equivalent of a light bulb being switched on for 1 hour; 2 Google searches generate as much energy as a kettle of tea… bearing in mind that 180 million searches are carried out every hour…
- One Google user generates 10kg of CO2 annually.
- Interesting fact: the Submarinecablemap site lists all the world’s submarine cables.
And meanwhile, on our planet:
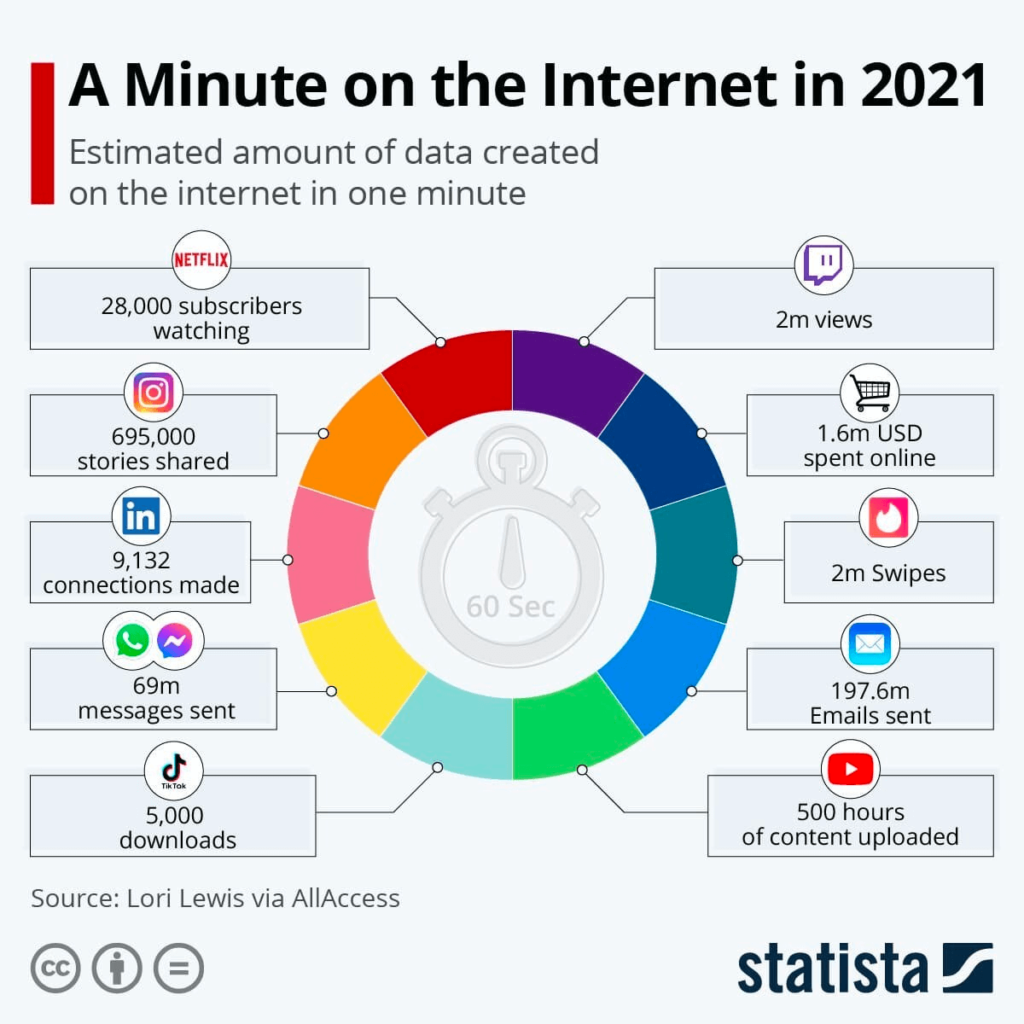
Given this technological cultural development, what are the most polluting digital sources in our daily activities?
1. Datas centers
Data centers and network infrastructures account for one-third of the world’s electricity consumption for new technologies and 53% of the greenhouse gases generated by digital technology. As an example, a 10’000 m2 data center consumes as much energy as a city of 50’000 inhabitants! Just the cooling alone requires 40% of the energy required.
However, we collect, store, and use more and more data, whether it is simple emails, files, or media, on our devices but also on the cloud. According to statistics, 90% of the data was created between 2015 and 2017. Another surprising and relatively worrying fact is that we produce as much information every two days as we did from the beginning of our civilization until 2003!
2. Digital and connected devices
Digital device production requires extracting rare, mostly non-renewable minerals. It is estimated that they contribute to 76% of the world’s natural resource depletion.
Manufacturing a smartphone, for example, requires 60 minerals and 80 times more energy to produce a gram of it compared to a gram of a car. According to a GreenIT study (2019), “greenhouse gases during this phase of extraction, manufacturing, and transportation of the final product account for 90% of the emissions generated during a phone’s life. The remaining 10% are emitted during the period of use when the phone is charging”.
By 2025, 48 billion connected objects should be in use on our planet, resulting in an environmental impact 3 times higher than in 2010, while contributing to nearly 40% of greenhouse gas emissions in the digital sector…
3. Video and streaming
Video accounts for 80% of the world’s digital data flow, of which nearly two-thirds are online video, mainly VOD (Video on Demand). According to the study conducted by The Shift Project, 300 million tons of CO2 might be generated by online video. This corresponds to the equivalent greenhouse gas emissions of Spain for one year.
As early as 2015, the Nouvel Observateur was alerting us, giving as an example the viewing of chat videos on social networks.
Were you aware that the 2.7 billion views of the Gangnam Style song represent the annual consumption of a small nuclear power plant?
4. Focus on social networks
In 2022, 4.7 billion social network users were counted worldwide, according to the annual We Are Social and Hootsuite survey.
One social network user emits up to 102kg of CO2, which is equivalent to driving 914km by car in a year.
Here’s a snapshot of daily data sharing by social network in 2019 (source: website Qu’est-ce qu’on fait ?!)
- Facebook: 350 million photos and 58 billion videos, or 645 million kg of CO2 per year, which is equivalent to 645’000 flights between Paris and New York.
- Instagram: 95 million photos and videos posted. One-third of the most viewed stories on Instagram are originated by brands for advertising purposes.
- Snapchat: 3 billion photos
- WhatsApp: 1.6 billion photos and 250 million videos
- Nearly 24 hours a month spent on YouTube and 23 hours on TikTok in 2022.
5. What about companies active in the digital sector?
If we take a look at the most digitally polluting companies with respect to their core business, we find giants like Amazon, Netflix, Spotify, and Pinterest… They are pointed at for using 30% of fossil energies against only 10% of renewable ones.
This includes the “good students”:
- Apple: their data centers have been 100% powered by renewable energy since 2013, followed by Google in 2018, and Facebook more recently. Microsoft is closer to 60%, like YouTube.
- Facebook has relocated some of its data centers to Sweden, while Microsoft submerges its data centers to promote natural cooling.
And the “bad students” according to the Greenpeace Clicking Clean report:
- Netflix, Amazon, HBO and Ulu;
- Netflix accounts for 13% of network capacity, which it fuels with 30% coal;
- Gaming and online/mobile gaming are also big consumers of energy and reach nearly 3 billion people.
II. What is responsible digital or eco-responsible digital?
Responsible digital, also called eco-responsible digital, consists in reducing the ecological, economic, and social footprint of all information and communication technologies. It implies an approach aiming at reducing energy consumption by adopting new behaviors in our digital habits.
This trend has many synonyms, such as green or sustainable computing, but also Green IT. According to the Greenly website, Green IT has two distinct shades:
- “Green for IT”: all technologies that allow companies to reduce IT’s environmental impact and therefore carbon footprint, by reducing their greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, etc.
- “IT for Green”: Socio-economic principles adopted, at the company and community levels, to initiate the ecological transition.
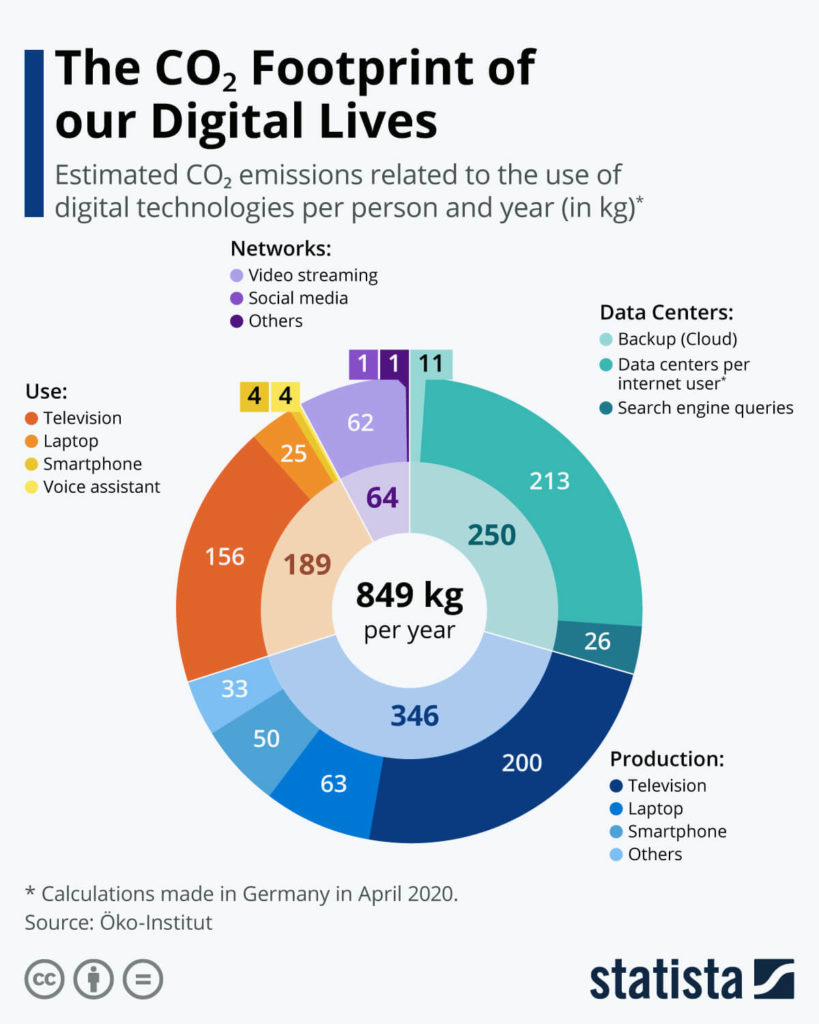
The GreenIT blog took a closer look at the annual consumption impact of a computer asset and the findings are impressive:
- 5,740 kWh of raw energy,
- 800 kg of greenhouse gases,
- 14,000 litres of water,
- 3kg of waste of electronic and electrical equipment.
- This is the equivalent of driving 9km or consuming 80 light bulbs every day.
3. What environmentally responsible digital strategy can we put in place at our level and in our companies?
The individuals’ awakening to the impact of our daily use of digital technology in our lives is relatively recent. It reaches a limited part of the population, which is more inclined to be surprised than worried.
What solutions and practices can we adopt to limit our impact on the planet?
1. Sorting out our emails
Whether at home or in the office, simple reflexes can be put in place to reduce our digital impact on the environment:
- Sort and delete your emails as you go along, knowing that 80% of emails are never opened!
- Empty your recycle bin
- Deactivate unnecessary newsletters, using tools such as Cleanfox or Mailstrom
- Archive important attachments on a hard drive
- Reduce your number of email recipients
- Avoid signatures with logos that add weight to your email
- Delete email accounts that you no longer use
- Use sites like WeTransfer to transfer large documents, which will be deleted after one week
2. Let’s use the Internet more wisely
Here are some simple tips to reduce the volume of searches or limit their impact:
- Save your most visited sites in your favorites, as they consume 4 times less energy
- Type the website name directly in the URL bar as opposed to the search bar
- Limit the number of tabs or programs opened, which constantly refresh
- Choose search engines with a more environmental dimension, such as Lilo (development of environmental and social projects), Ecosia (contributing to reforestation: 45 queries = 1 tree), Ecogine or Ecosearch
- Reduce your streaming and video viewing, which generate 300 million tons of CO2
- Install the Carbonalyser extension to your web browser, to monitor your electricity consumption and climate impact
3. Let’s adopt new eco-friendly uses
In 2022, more than 2/3 of the world’s population owned a mobile phone, i.e., 5.34 billion people! More than 92% of them access the Internet via their mobile, according to a Hootsuite and We Are Social survey of July 2022.
- Limit the applications you load on your mobile or delete those not in use
- Back up your photos and files on an external hard drive rather than on the cloud
- Connect via Wi-Fi rather than 4G or 5G, which consume 5 to 25 times more energy
- Turn off Wi-Fi, GPS, or Bluetooth functions when you don’t need them
- Resist the urge to buy the latest model of your favorite mobile or tablet brand: by extending their lifespan from 2 to 4 years, you will improve their ecological footprint by 50%.
- Choose to buy physical video games rather than digital ones
- Repair or buy reconditioned second-hand products: while telephones are replaced on average every 2 years, only 5% of digital devices are recycled; the others end up being burned
- Watch television via DTT rather than ADSL
- Turn off your devices at night: it’s good for the planet and battery life
4. Let’s think about the environmental impact in our companies
Any company can adopt the above-mentioned habits and act on other technological or technical variables:
- Have your website hosted by companies like Infomaniak, offsetting their activities.
- Install eco-friendly search browsers, such as Ecosia or Lilo.
- Use plugins to improve the performance of your WordPress site. The GT Metrix tool allows you to identify the main areas for improvement.
- Track your carbon footprint in real-time on dashboards provided by companies like Greenly
- Put in place a process to obtain the “Label Numérique Responsable”.
- Design a green website: by being lighter, Google will favor it in natural search.
- Green SEO: sorting and cleaning obsolete content, optimizing and improving page loading time, etc.
- Promote responsible marketing by developing advertising campaigns based on a mission/impact with environmental and societal projects (e.g. Gooded).
Investing in CSR is always a good strategy for a company:
- It benefits your image in the eyes of your customers: 80% of French people would be more loyal to a brand if it committed to fighting digital pollution
- It is more motivating and engaging for your employees to work for a company that defends a cause. It gives a sense of purpose to their job, creates an impact, etc.
CONCLUSION:
According to the Shift Project in 2019, if the Internet were a country, it would be the 3rd largest electricity consumer in the world, after China and the USA. This a powerful insight that highlights the importance of digital technology and the impact of our behavior on the planet.
This is a significant factor that all companies should integrate into their operations and development while involving all stakeholders, whether they are employees, customers, or users.
Let’s discuss how Eminence can offer you environmentally responsible solutions for your web and digital projects.

