Marketing is a constantly changing field where every choice has significant implications and requires justification. In this dynamic landscape, evaluating performance is essential for success.
Return on Investment, commonly known as ROI, is a vital metric in both marketing and the broader business context. It evaluates the efficiency and profitability of an investment or expenditure. Specifically, in marketing, ROI is employed to gauge the effectiveness of a campaign by contrasting its costs to the revenue it produces.
Join us as we delve into its computation method, examine factors influencing it, and discuss strategies to enhance it for sustained performance.
Prerequisites for Evaluating Your ROI
ROI is a vital metric that assists in identifying the most lucrative marketing investments, enabling you to adjust expenditures as needed. Yet, for this KPI to hold significance, it should align with your goals and crucially, be quantifiably measurable.
Defining Your Campaign Objectives
Assessing a ratio is only significant when you’ve established clear objectives prior to initiating your marketing campaign. These objectives act as a guiding compass for your strategy, simplifying its monitoring and performance evaluation.
You may be familiar with the SMART method for goal setting, which emphasizes objectives to be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound.
Collecting Data for ROI Calculation
Calculating ROI hinges on effective data collection to gauge your campaign’s impact.
To do this, it’s essential to employ tracking tools that capture diverse data, from sales and conversions to web traffic, social media engagement, and email marketing.
Some key tools include:
- Google Analytics 4: offers browsing tracking while maintaining user privacy.
- Adobe Analytics: provides real-time insights and detailed audience segmentation.
- Social media monitoring tools, like those from Meta and LinkedIn.
- Platforms for managing advertising campaigns.
To make these tools effective, they should be configured to connect with your ad campaigns using tracking markers, like UTM tags.
It’s important to be aware that if users decline cookies on your site, it can impact the data gathered.
Lastly, consolidate all the acquired data into dashboards for a comprehensive analysis.
Calculating the Cost of Your Campaigns
When analyzing the Return on Investment (ROI) of your marketing endeavor, it’s crucial to distinguish between the various costs associated with your campaign: direct and indirect.
- Direct costs cover expenditures immediately tied to the campaign, including advertising expenses, promotions specific to the campaign, distribution fees, and more.
- Indirect costs, on the other hand, might not be immediately tied to the campaign but can influence its outcomes. These span the broader operational costs like salaries for the marketing team, overheads, and expenses linked to managing your website or social channels.
- Costs associated with advertising mediums, such as Google Ads or Facebook Ads, are expenditures for paid promotions across online platforms. These often make up a considerable chunk of the marketing budget and can be tweaked based on the efficacy of each ad channel.
Read more: Increase the ROI of your Google Ads campaigns with call tracking and conversational intelligence
- Costs associated with content creation are pivotal for content marketing and social media. They encompass expenses incurred in crafting written, visual, or multimedia materials, like blog posts, videos, and infographics. The cost spectrum for such content can fluctuate based on its intricacy and caliber.
- Budget allocations for teams and tools essential for campaign oversight account for aspects like salaries, benefits, fees for consultants, and subscriptions to software and specialized marketing utilities.
Calculating Generated Revenue
For a precise calculation of your marketing campaign’s ROI, it’s advised to distinguish between direct and indirect earnings:
- Direct revenue stems directly from the marketing initiative, like sales from unique promotional codes related to the campaign or purchases from online ad clicks.
- Indirect revenue, meanwhile, is influenced by the campaign but isn’t directly traceable, like subsequent sales from clients initially acquired during the campaign.
How to Accurately Measure Generated Revenue
To trace the source of your sales, it’s essential to set up a system for conversion tracking and attribution (encompassing sales, leads, and more) linked to the influencing marketing campaigns.
Utilize attribution instruments like tracking cookies, conversion pixels, and UTM codes to monitor users’ pathways, starting from their first engagement with the campaign to the ultimate conversion. This enables you to determine the exact influence of the campaign on your earnings.
The Importance of Incremental Sales
Incremental sales refer to those sales that wouldn’t have transpired without the specific marketing initiative. To gauge the campaign’s influence, it’s valuable to juxtapose its outcomes with a timeframe devoid of any campaign activity.
Evaluating incremental sales lets you pinpoint the true potency of the campaign, leading to a more accurate ROI calculation. Such assessment is especially critical for campaigns aimed at customer retention, where the objective is to enhance sales among current clientele.
Read also : How to use a CRM to improve ROI?
Calculating ROI and ROAS
ROI considers all expenses tied to a marketing campaign, such as costs for content creation and team-related expenditures, to determine the campaign’s overall profitability. On the other hand, ROAS (Return on Advertising Spend) zeroes in exclusively on the revenue stemming from advertising outlays.
ROI Calculation Formula (%)

- “Generated Revenue” includes all direct and indirect revenue attributable to the marketing campaign, such as sales, leads, etc.
- “Campaign Costs” include all expenses related to planning, implementation, and management of the campaign, including both direct and indirect costs.
=> A positive ROI signifies a profitable campaign, whereas a negative ROI points to a loss. Thus, an ROI of zero implies that the revenue produced matched the campaign expenses.
ROAS Calculation Formula
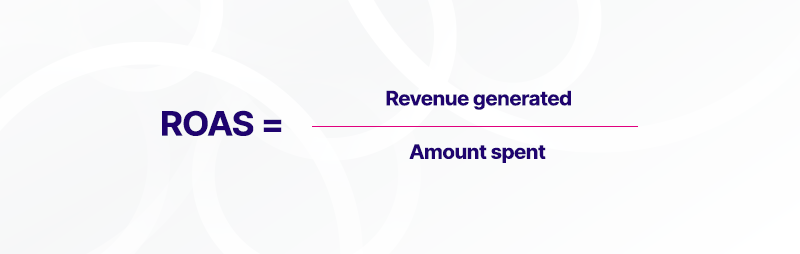
While ROI is usually conveyed as a percentage, ROAS is often presented as a ratio. For instance, a ROAS of 5 suggests that every euro invested in advertising yielded 5 euros in returns.
ROI offers a holistic perspective on the profitability of marketing endeavours, whereas ROAS zeroes in on the efficacy of specific advertising avenues.
Employing both ROI and ROAS concurrently grants a fuller understanding of your marketing’s overall efficacy.
Tools and Software to Simplify ROI Calculation
Computing ROI can be streamlined with the aid of dedicated tools and software that facilitate data collection, ensure precise calculations, and monitor campaign outcomes.
Selecting the optimal tool hinges on factors like your company’s scale, budget, campaign goals, and the intricacy of your tracking and reporting requirements.
Analyzing and Optimizing Campaign Impact
Short-Term vs. Long-Term ROI Analysis
The effectiveness of a marketing campaign can fluctuate with time: some might yield instant outcomes, whereas others might resonate more in the long run.
For numerous enterprises, the genuine merit of marketing endeavors is anchored in sustaining customer loyalty. Emphasis is placed on enduring results, considering its three times as cost-effective to retain an existing customer than to onboard a new one.
Several strategies can be employed to achieve this, such as:
- Fostering bespoke connections via loyalty schemes, VIP circles, and exclusive updates,
- Sustaining consistent engagement through newsletters, interactions on social media, and competitions,
- Reigniting engagement with inactive customers using marketing automation and special deals.
Our Advice: Combine CRM and Marketing Automation!
Improving ROI: A Long-Term Comprehensive Strategy
To optimize ROI over an extended period, it’s vital to employ enduring and synergistic business tactics, including:
- Enhancing the quality of products or services,
- Cultivating robust customer rapport,
- Modifying campaigns in response to market shifts.
Harmonizing your marketing goals with overarching business aspirations can pave the way to triumph.
ROI insights aren’t solely beneficial for gauging previous campaign achievements; they also serve as a pivotal tool for shaping current and future strategies.
- For the now: It’s about refining your campaign in real-time based on its outcomes. This might involve prioritizing top-performing ad channels, tailoring communications for distinct groups, or augmenting content quality. A/B testing is an apt tool for such enhancements.
- Looking ahead: Continual monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) and data scrutiny can spotlight areas for enhancement, from altering webpage elements (like headlines or visuals) to user pathways and advertisements.
In conclusion
ROI transcends a mere mathematical equation; it empowers you to gauge, scrutinize, and refine your marketing endeavors to realize substantial returns.
Understanding the distinction between ROI and ROAS positions you advantageously to assess both your advertising and overarching marketing campaign effectiveness.
As an agency adept in data and customer acquisition, Eminence offers its proficiency in orchestrating awareness or conversion ad campaigns and fine-tuning them.

