At a time when online sales account for 19% of retail sales worldwide and hybrid work is a given, the safety of users and companies has become paramount.
Every year, there are 978 million people affected by a cyber-attack around the world, with damages estimated at $6 trillion in 2021 and expected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025! (Source: Cybersecurity Ventures)
An exorbitant cost that reflects this major risk, affecting both SMEs and large companies in their activities, but also individuals in their personal lives.
Through this article on a topic as vast as it is exciting, we will focus on the main risks and threats related to cybersecurity and data protection. We will then present the points of vigilance and solutions to be put in place for companies and individuals.
The main safety risks in 2022
We are currently in a period of geopolitical and economic tension, conducive to cyber criminals’ attacks and hacks. At the same time, the threat is heightened by the complexity for companies to secure their systems and infrastructures that are now distributed and shared around the world.
In an article by Betanews, we learn that cybercriminals are able to penetrate 93% of organizational networks and thus access their local network.
What are the main cyber-attack threats identified, in particular by Gartner, an American consulting and research company in the field of advanced techniques?
- The surface of attack : the larger a company is in terms of geography, activities, software, clouds, etc., the more opportunities there are for it to be attacked at different angles;
- The digital supply chain: supply chain data attacks will be multiplied by 3 between 2021 and 2025;
- Software supply chain: attacks on IT subcontractors against Saas suppliers and their customers;
- Linux operating systems: they are regularly targeted, as are connected objects running on this system;
- Cloud attacks and Sharepoints: Violations have affected 79% of businesses since 2020. An attraction for criminals, when we estimate at 92% the companies that host part of their data or IT environment on the cloud;
- Identity Threat Detection & Response (ITDR): attempts and intrusions into identity and access management systems, requiring the integration of new tools to cope;
- Human errors: still too many, they remain one of the main factors in data and system violations. Phishing, spearing or social engineering (social engineering or psychological manipulation) are all methods used by cybercriminals to spread viruses or break into a computer system. 94% of malware (malware) is sent by e-mail;
- Usage: 70% of employees use professional devices for personal reasons, while 37% of employees use their personal computers to connect to professional applications.
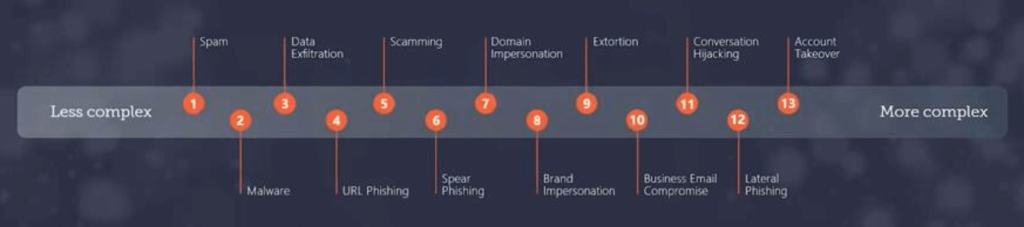
The Impact of Cyber Attacks on Businesses
The repercussions of an attack can be fatal for a company, because beyond the financial losses induced for the company, the collateral impacts can be equally damaging, especially in terms of loss of customer data and the resulting e-reputation.

In this Halloween season, here are some chilling statistics:
- More than one in two companies was the subject of a cyber attack in France in 2021 (source: CESIN Security Barometer);
- Ransomware attacks have been multiplied by 2.5 (software holding our data hostage for ransom), according to ANSSI;
- The median cost is estimated at €50,000 due to the interruption or disruption of business, the deterioration of computer equipment, data leakage, the impact on the e-reputation of the company and its brands, the risk of loss of confidentiality, legal fees, etc.;
- An average loss of 27% of annual turnover;
- A 21% production disruption;
- Business interruption of at least 8 hours for 40% of SMEs following a cyber attack.
Read also
→ New nFADP Regulation in Switzerland: Principles and Impacts on Your Digital Strategy
Moreover, 60% of the SMEs attacked fail to recover and are forced to file for bankruptcy within 18 months of the attack in France.
How can data protection risks be mitigated?
In the face of these attacks orchestrated by real criminal organizations, motivated by rates of return on investment of the order of 200 to 800%, according to the consulting firm Wavestone, solutions exist to protect against them.
According to Verizon, 71% of cyberattacks are motivated by the financial aspect, rather than intellectual property theft and espionage. It is not uncommon for hackers to demand a ransom in exchange for stolen data.

What data protection should be implemented internally?
- The installation of anti-virus;
- Integration of an API into the messaging environment directly to protect individual inboxes. It can also trace communication patterns and detect anomalies using available data and artificial intelligence;
- The implementation of security gateways on mail servers, to filter and block malicious content, such as suspicious IP or URL, virus and malware probabilities;
- Setting up firewalls to secure connections to websites and incoming and outgoing network traffic;
- Regular data backups to minimize risks by restoring old data;
- Data encryption to guarantee the confidentiality of information;
- The control of authorizations and the principle of least privilege (PMP) in the management of administrative accounts in the networks of customers, consisting in giving only the strictly necessary accesses;
- Updating software, applications and operating systems to avoid identified vulnerabilities;
- The security and technological information monitoring to know the latest recommendations and points of vigilance, via ANSSI for example;
- The use of security audits and intrusion testing to measure the vulnerability of the system.
How can you secure your website and interactions with users?
- The use of HTTPS protocol to encrypt all data, in particular online payments;
- The use of Captcha (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) for any form, in order to drive out robots;
- The proposal of complex passwords, which can be placed in a safe like Lastpass, because 61% of violations are due to weaknesses in passwords or identification information. Ensure they are renewed regularly and diversified according to sites and accounts. Double authentication can also be an additional security guarantee;
- Limitation of cookies: the more we allow cookies within the framework of the GDPR, the more our data can be disseminated and risk of being hacked. Note that GA4 (Google Analytics) no longer keeps IP addresses and will put an end to third-party cookies during 2024, with the deployment of the Sandbox Privacy.
The importance of raising awareness about the risks of cybercrime in business
- Information to staff: 47% of teleworkers were trapped by phishing attempts. Therefore, the setting up of meetings, trainings and simulation workshops is essential to explain the risks and the different types of attack that employees can be victims of, in their professional and even personal lives with digitalization, social networks (e-reputation), clouds, etc.
- Raising awareness among small businesses: for lack of means and knowledge, they are often the main victims. Large companies can thus play the role of informant adviser to their suppliers, subcontractors, partners, etc.
To limit the financial impact of attacks, there are professional cyber liability insurance. As a result of increased mischief, premiums are increasing and exclusion criteria are numerous (such as ransom payments).
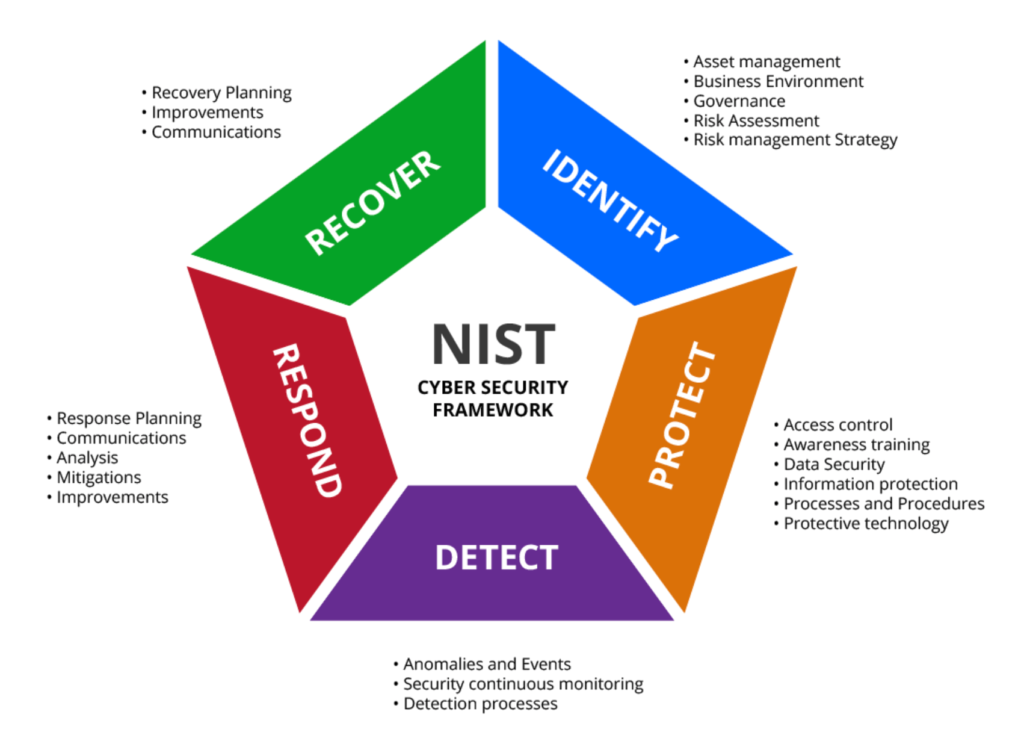
NIST Cyber Security Repository (National Institute of Standards and Technology)
It is based on three pillars:
- PROTECTING: Cyber Protection
- DETECT: Cyber Defence
- RESPONDING: Cyber Resistance
“Cyber attacks are like natural disasters. There is no way to prevent a hurricane from hitting your city, but you can certainly prepare for it.”
CONCLUSION :
Cyberattack techniques are evolving rapidly with ever more varied means and methods. During COVID, 35% of attacks were still unknown compared to 20% previously. It is therefore no coincidence that the risks related to cybersecurity are in the Top 3 of Risk Managers, whereas they were only in 7th place in 2017.
“The CFOs are starting to see what it’s going to cost if they don’t protect themselves, not just the extra cost.” (Guillaume Poupard, ANSSI).
Cybercrime now resembles a real industry because of its scope and the financial impacts at stake. It has become vital for businesses to prevent this by anticipating, ensuring and investing in the security of their systems, but above all by informing and educating their teams about cybersecurity.

