Overview
With the rise of e-commerce and the digitalization of services and businesses, the customer journey has now become an essential component of a comprehensive marketing strategy. According to the Euromonitor institute, spending related to the experience economy is expected to reach $8.2 trillion by 2028!
This article explores the interests and challenges of the customer journey before presenting the five key stages of the customer journey, to transpose it into an e- commerce site logic.
The Customer Journey: An Essential Parameter of Your Digital Strategy
What is a Customer Journey?
The Customer Journey or customer experience refers to the path taken by a customer during their purchasing process of a service or product. It begins with information
search up to the transaction, but can continue beyond through the use of after-sales services and customer loyalty.
The Birth of the Customer Journey Concept
The concept of experience economy was discussed by Joe Pine and Jim Gilmore, authors of the article "Welcome to the Experience Economy," published in the Harvard Business Review in 1998. It refers to value creation through the addition of emotions and feelings in the purchasing process, to make it unique and pleasant.
But long before being democratized under this term, the notion of customer experience had existed for many years in different forms: loyalty cards, customer service, partnerships and co-branding, in-store journeys, etc.
The Rise of Customer Experience: A Financial Challenge
In an ultra-competitive universe, a company generally has few options:
- Cut prices and increase volume to be profitable
- Position itself in a niche or in a blue ocean and target the high-end market
- Diversify its sales channels to maximize its customer potential
- Create value by offering additional services or a unique experience allowing it to increase its prices: perceived value
This last strategy has many advantages:
- Improved visibility, image (e-reputation) and brand awareness
- Better customer relationships
- More loyalty and customer retention
- Increased organic traffic
- Revenue growth through customer focus
Faced with these challenges, in recent years, dedicated services have emerged in large companies to make the customer journey a real competitive advantage.
Focusing on the Customer: A Reassurance Factor
While we are confronted daily with 1,200 advertising messages, 6 times more than in the 1980s, being present is no longer sufficient. You must be seen and inspire confidence. (Source: pqmedia study)
It becomes increasingly difficult to convert our visitors into customers, who are looking for more humanity and trust from brands. They want a company that listens to them,
while solving their problems. Before deciding to buy a product, the customer conducts intensive research on products, but also on social proof concerning companies (evaluations and reviews). This is called the messy middle.
This is why brands focus their efforts on producing high-quality, relevant and creative content to stand out and reassure consumers. The customer journey must take these parameters into account in its creation thinking.
The 5 Stages of the Customer Journey
The customer journey comprises five different stages grouped as follows:
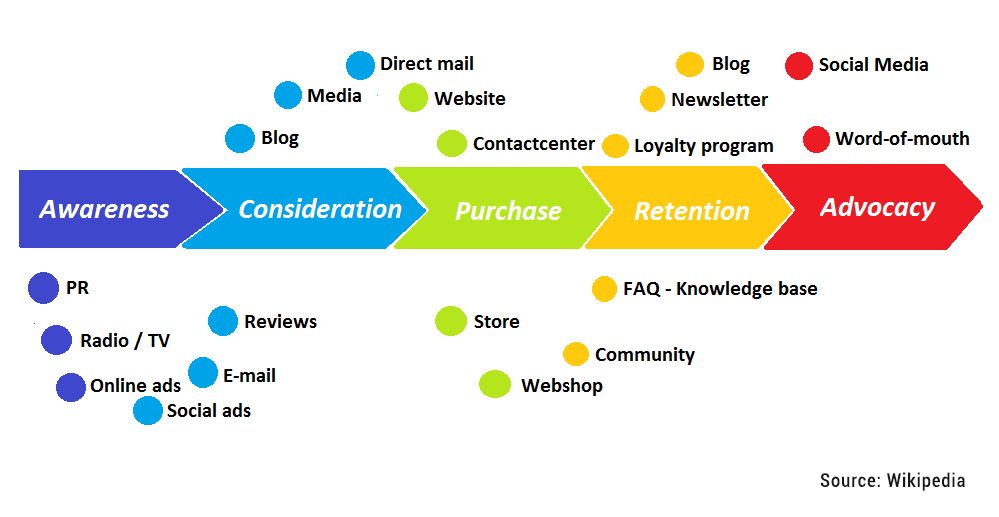
Awareness Stage – Make Your Products or Services Known!
In the first stage of the Customer Journey, your customer develops an interest in a product. They begin to collect information using different sources. During this stage, you should focus on your customer's problems and needs rather than emphasizing your solutions and products.
For the awareness stage, the following materials could be useful to your customer:
- Creative videos
- Informative white papers
- Relevant reviews and evaluations
- Interesting studies
- Meaningful graphics
Consideration Stage – Interest in Your Product is Reinforced
Once your potential customer has had the first impression and received information, they normally don't buy immediately. They will compare, examine and verify – and this is where the second stage begins, the consideration stage.
During this stage, you must accompany your customer in their choice and provide them with all the useful information they need. At this stage, marketing automation can prove very useful as it allows providing the customer with the right content at the right time.
Decision Stage – The Customer Buys the Product
Finally, the moment comes when the customer decides to buy your product. Important factors for the customer at this stage are support and of course price. As soon as the
potential customer has become an active customer and purchased your product, the journey is not over, but on the contrary, another door opens.
Service Stage
The service stage is the stage where the customer uses the product and, if necessary, receives other services. During this stage, the customer will be satisfied with their purchase or not.
If yes, they will make another purchase and may also recommend you, but in case of negative appreciation, they won't hesitate to make it known by giving their opinion and commenting on their bad experience on the web and social networks. You must therefore anticipate, thank them for their purchase and show that you are listening by offering them solutions.
Loyalty Stage
In the loyalty stage, your customer is satisfied with their purchase and uses your product or services. They also recommend your product or company, either directly in their environment or on digital platforms such as Facebook, Instagram or on your website. Consequently, your customer's recommendations will guide other potential customers in their customer journey. Don't hesitate to thank them, offer them to join VIP customers or become ambassadors.

Subscribe to our newsletter and gain access to strategic insights, exclusive analyses, and expert tips to enhance your online presence.
Customer Journey Examples
Customer Journey Examples by Sector
Understanding customer journeys is significantly enriched through the study of concrete examples. Each business sector presents specificities that directly influence the customer experience and journey stages.
Customer Journey in SaaS: The Slack Example
The customer journey in the SaaS sector is characterized by a self-service process and a focus on progressive adoption. Typical stages include:
- Awareness: Discovery via content marketing or team recommendations
- Consideration: Feature evaluation with interactive demonstrations
- Trial: Free trial period of 14-30 days
- Adoption: Guided onboarding with step-by-step tutorials
- Expansion: Invitation of other users and upgrade to paid subscription
The particularity of SaaS lies in the crucial importance of onboarding. Slack uses a gamified approach with intelligent notifications to encourage adoption and facilitate integration with other tools.
Banking Customer Journey: Account Opening
The banking sector imposes regulatory constraints that structure the customer journey. The stages include:
- Need awakening: Triggers like moving or dissatisfaction
- Research: Offer comparison via comparison sites
- Evaluation: Rate analysis and agency proximity
- Application: Appointment scheduling and file constitution
- Verification: Regulatory KYC (Know Your Customer) process
- Activation: Receipt of payment methods and first uses
Omnichannel is essential in this sector, with journeys that navigate between physical agency, web and mobile. Moments of truth include the delay in obtaining payment methods and the quality of the mobile application.
E-commerce: ASOS Optimization
The e-commerce journey focuses on reducing cart abandonment (70% abandonment on average). ASOS solved this challenge by optimizing its stages:
- Inspiration: Need discovery via social networks
- Research: Product comparison and review reading
- Evaluation: Price/quality analysis
- Purchase: Simplified ordering process
- Delivery: Real-time tracking
- Loyalty: Personalized recommendation programs
ASOS's solution included guest checkout, multiple payment options and security reassurance, significantly reducing cart abandonment.
Hospitality: Marriott Innovation
The hotel sector presents a long decision cycle with a strong emotional charge. Marriott develops a digital approach for its stages:
- Inspiration: Travel trigger
- Planning: Comparative accommodation research
- Reservation: Optimized booking process
- Preparation: Mobile check-in and personalization
- Stay: Mobile application for services
- Post-stay: Satisfaction surveys and loyalty programs
Marriott uses AI to personalize the experience and integrates IoT to automate room services.
Restaurant: The Multichannel Approach
The restaurant sector develops omnichannel journeys integrating on-site, delivery and take-away. Optimized stages include:
- Trigger: Hunger or social occasion
- Research: Menu consultation and reviews
- Order: Adapted channel selection
- Preparation: Real-time order tracking
- Consumption: Multichannel meal experience
- Evaluation: Feedback and loyalty
Identified moments of truth include service speed, product freshness and fluidity between channels.
Customer Journey in Digital Marketing
The Customer Journey in the Digital Marketing Era
Digital marketing fundamentally transforms customer journeys, creating non-linear and omnichannel experiences that differ radically from traditional approaches.
Differences Between Digital and Traditional Journeys
The traditional journey follows a linear model: advertising exposure → store visit →
purchase. The digital journey is characterized by:
- Non-linear navigation: Customers navigate between different channels and devices
- Multiple touchpoints: Website, social networks, email, mobile applications
- Real-time personalization: Dynamically adapted experiences
- Rich behavioral data: Complete tracking of interactions
73% of consumers use multiple channels during their purchasing journey, and 87% of buyers start their research online.
Essential Digital Touchpoints
The digital customer journey is built around specific touchpoints:
Bidirectional channels:
- Social networks (Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn)
- Website and mobile applications
- Personalized email marketing
- Live chat and chatbots
- Instant messaging (WhatsApp, Messenger)
Unidirectional channels:
- Display and video advertising
- SEO/SEM and search results
- Content marketing (blog, videos, podcasts)
- Mobile push notifications
Emerging innovations:
- Voice commerce (Alexa, Google Assistant)
- Augmented reality for virtual try-ons
- Integrated social commerce
- Digital avatars and virtual assistants
Digital Customer Journey Stages
The digital journey is structured in five optimized stages:
- Awareness: Brand awareness generation via social networks and search engines
- Consideration: Product comparison with interactive tools and customer reviews
- Decision: Checkout optimization and secure payments
- Retention: Loyalty programs and post-purchase follow-up
- Advocacy: Transformation into ambassadors via social networks
Each stage requires specific KPIs: impressions for awareness, engagement rate for consideration, conversion rate for decision, CLV for retention, and NPS for advocacy.
Omnichannel and Integrated Journey
The omnichannel approach offers a consistent experience across all channels. Omnichannel customers spend 4 times more than single-channel customers.
Key characteristics:
- Data integration: Unified customer vision
- Experiential consistency: Harmonized messaging
- Personalization: Adapted to profile and history
- Continuity: Journey resumption on different devices
50% of consumers prefer "Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store" (BOPIS), illustrating the importance of physical-digital integration.
2025 Trends in Digital Marketing
Artificial Intelligence:
- Hyper-personalization: Real-time AI recommendations
- Advanced chatbots: 5% of consumers accept AI for fast service
- Predictive analysis: Anticipation of customer needs
Augmented Reality:
- Virtual try-ons: Fashion, beauty, furniture
- Spatial commerce: Apple Vision Pro, Meta Quest
Mobile-first:
- 43% of e-commerce sales will be mobile in 2024
- Mobile payments: Mass adoption
- Geolocation: Contextual experiences
Social Commerce:
- Livestream shopping: 30% conversion rate
- Influencers: Authentication and recommendations
- Social networks: Direct purchase platforms
The AI marketing market will reach $107.5 billion USD by 2028, confirming the growing importance of these technologies in optimizing digital customer journeys.
How to Analyze the Customer Journey?
Complete Customer Journey Analysis Methodology
Customer journey analysis is a strategic process that allows understanding and optimizing each customer interaction. This analysis goes beyond simple mapping to examine the impact of each touchpoint on decisions and behaviors.
Fundamental Analysis Methods
- 5-Step Framework: The most commonly used structures analysis around Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy.
- Jobs-to-be-Done Framework: Focuses on the "jobs" that customers try to accomplish during their interactions with your product or service.
- Touchpoint Analysis: Maps all contact points to identify improvement opportunities.
- Customer Empathy Mapping: Understands customer emotions and behaviors by mapping their experience from their perspective.
Longitudinal analysis is essential to understand how customers evolve over time, capturing behavioral patterns, emotional variations and cumulative impact of interactions.
Data Collection Techniques
Qualitative methods:
- Customer interviews: Direct exploration of experiences and motivations
- Diary Studies: Capture experiences in their natural context
- Focus groups: Discovery of common pain points
- Direct observation: Behavioral field studies
Quantitative methods:
- Web Analytics: Bounce rate, time spent, navigation paths
- Quantitative surveys: CSAT, NPS, Customer Effort Score scores
- Operational data: Performance metrics, support logs
Critical distinction: Explicit feedback (surveys, questionnaires) and implicit feedback (behavioral data, social mentions) offer essential complementary perspectives.
Tools and Analysis Technologies
Visualization tools:
- Lucidchart: Real-time collaboration with templates
- UXPressia: Complete platform with personas and impact maps
- Miro/FigJam: Collaborative whiteboards
Behavioral analytics:
- Google Analytics 4: Conversion tracking and journey analysis
- Hotjar: Heatmaps and session recordings
- Adobe Customer Journey Analytics: Real-time omnichannel analysis
Feedback and listening:
- Medallia: Experience intelligence with conversation analytics
- Qualtrics: Complete customer experience management suite
- InMoment: AI-powered feedback
4-Phases Analysis Process
Phase 1: Preparation
- Define SMART objectives
- Identify target personas
- Determine analysis scope
- Assemble cross-functional team
Phase 2: Collection
- Audit existing data (analytics, CRM, support)
- Qualitative research (interviews, observations)
- Quantitative collection (surveys, metrics)
- Multi-source aggregation
Phase 3: Analysis
- Current journey mapping
- Behavioral pattern identification
- Emotion and high/low analysis
- Correlation with business KPIs
Phase 4: Action
- Insight prioritization by impact/feasibility
- Concrete solution development
- Change implementation
- Results measurement and ROI
Friction Point Identification
Types of pain points:
- Interaction pain points: Specific usability problems
- Journey pain points: Difficulties in accomplishing objectives
- Relational pain points: Long-term relationship problems with the brand
Identification methods:
- Funnel analysis: Drop-off points
- Heatmaps: Visualization of problematic behaviors
- Customer feedback analysis: Analysis of comments and complaints
- Support ticket analysis: Recurring problems
- Mystery shopping: Customer experience testing
Pain point prioritization according to: Impact on journey and frequency of occurrence, severity of frustration caused, resolution feasibility, business impact on key metrics.
Subscribe to our newsletter and gain access to strategic insights, exclusive analyses, and expert tips to enhance your online presence.
KPIs and Analysis Metrics
By journey stage:
- Awareness: Web traffic, social reach, brand mentions
- Consideration: Engagement rate, time spent, downloads
- Decision: Conversion rate, AOV, cart abandonment
- Retention: Retention rate, CLV, churn rate
- Advocacy: NPS, recommendation rate, UGC
Transversal metrics:
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Satisfaction per interaction
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Effort required to accomplish a task
- First Contact Resolution: Resolution from first contact
- Time to Resolution: Average problem resolution time
How to Improve Service Quality Through Customer Journey Analysis?
Leveraging Customer Journey Insights for Service Enhancement
Customer journey analysis provides invaluable insights for improving service quality across all touchpoints. By understanding customer experiences holistically, organizations can identify specific areas for enhancement and implement targeted improvements.
Service Quality Assessment Through Journey Mapping
Identifying Service Gaps:
- Map current service delivery against customer expectations at each stage
- Analyze emotional highs and lows throughout the journey
- Identify moments where service falls short of customer needs
- Benchmark service quality against industry standards
Critical Service Moments:
- Moment of Truth: Points where service quality significantly impacts customer perception
- Pain Point Analysis: Identifying where service breakdowns occur most frequently
- Effort Assessment: Measuring customer effort required at each service interaction
- Resolution Tracking: Monitoring how effectively issues are resolved
Data-Driven Service Improvements
Performance Metrics Integration:
- First Call Resolution (FCR): Percentage of issues resolved on first contact
- Average Handle Time (AHT): Time efficiency while maintaining quality
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Service-specific satisfaction scores
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Overall service advocacy measurement
Predictive Service Analytics:
- Use journey data to anticipate customer needs
- Implement proactive service interventions
- Identify customers at risk of churn
- Optimize resource allocation based on journey insights
Service Personalization Strategies
Contextual Service Delivery:
- Tailor service approach based on customer journey stage
- Provide relevant information at the right time
- Adapt communication style to customer preferences
- Offer personalized solutions based on journey history
Omnichannel Service Consistency:
- Ensure seamless service experience across all channels
- Maintain context when customers switch between touchpoints
- Provide consistent service quality regardless of interaction method
- Enable smooth handoffs between service channels
Continuous Service Optimization
Feedback Loop Implementation:
- Collect real-time feedback at key journey moments
- Implement rapid response mechanisms for service issues
- Use customer insights to refine service processes
- Create customer advisory panels for ongoing improvement
Service Innovation Through Journey Insights:
- Identify opportunities for new service offerings
- Develop self-service options based on customer behavior
- Implement AI and automation for routine service tasks
- Create value-added services that enhance the journey
The Customer Journey in E-commerce
The golden rule according to Steve Jobs is to design a purchasing journey corresponding to your targets and personas, and not according to your technology. The reflection is therefore carried out from downstream (potential customers) to upstream (the company and its products).
Create Your Personas: The Portrait of Your Target Customers
Personas are the representation of your typical potential customer: their age and profession, their story and hobbies, their aspirations and frustrations, the networks or tools they use. The objective? Make your "targets" human, in order to better understand their behavior, their expectations and provide a solution to their needs.
How to Create Your Buyer Persona?
We recommend creating 3 to 5 personas to start, then multiplying them if needed, once you have managed to properly identify their journey and its components.
Create a User Journey Map: The Customer Journey Map
The customer journey map aims to imagine and visualize your customer's journey on your website or mobile application. The following information must be mentioned:
- The persona corresponding to the map created
- The description and objectives of the different stages: the scenario
- The information and purchase process stages: evolution on the site
- Contact points with your company: interactions
- Emotions felt and possible frustration points (pain points)
- Possible questions and expectations to anticipate and fulfill
How to Create a Customer Journey Map?
Note that each customer journey map must be regularly revised and optimized, since the market and technologies evolve rapidly.
The Importance of Contact Points to Identify
Contact points are the stages during which the "buyer persona" comes into contact with the company and which trigger an action. Here are some examples of contact points during the customer journey:
- Social networks (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, )
- Website
- App
- Events and exhibitions
- Television or radio advertising
- Flyers (print media)
The Moment of Truth: The Decisive Point of the Journey
The moment of truth is a crucial point in the journey where the customer will decide whether to continue their experience with our company, such as contacting us or making a purchase, or abandon their interactions and end their navigation.
These decisive moments must imperatively be measured and evaluated, for example using Google Analytics, in order to know at which stage of the journey the customer left. This is to be able to detect possible problems (technical, logistical, etc.) and provide a solution or propose an appropriate marketing follow-up, such as with marketing automation.
FAQs
What Makes a Good Customer Journey?
A good customer journey is characterized by several key elements:
Seamless Experience:
- Smooth transitions between different touchpoints
- Consistent messaging across all channels
- Minimal friction and obstacles
- Clear and intuitive navigation
Customer-Centric Design:
- Focus on customer needs rather than business processes
- Personalized experiences based on customer preferences
- Relevant content delivered at the right time
- Solutions that address real customer pain points
Emotional Connection:
- Moments of delight that exceed expectations
- Empathetic responses to customer concerns
- Brand personality that resonates with target audience
- Positive emotional associations throughout the journey
Measurable Outcomes:
- Clear conversion goals at each stage
- Trackable customer behaviors and interactions
- Continuous improvement based on data insights
- ROI measurement for journey optimization efforts How to
Improve Your Customer Buying Journey
Data-Driven Optimization:
- Analyze customer behavior patterns using analytics tools
- Identify drop-off points and friction areas
- A/B test different journey elements
- Use customer feedback to guide improvements
Personalization Strategies:
- Segment customers based on behavior and preferences
- Deliver relevant content and offers
- Customize communication timing and channels
- Implement dynamic content based on journey stage
Technology Integration:
- Implement marketing automation for timely interactions
- Use AI for predictive customer behavior analysis
- Integrate CRM systems for comprehensive customer views
- Deploy chatbots for instant customer support
Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Align marketing, sales, and customer service teams
- Share customer insights across departments
- Create unified customer experience standards
- Establish feedback loops between teams
What is Journey Mapping?
Journey mapping is a visual representation of the customer experience that captures the complete process customers go through when interacting with your brand.
Key Components:
- Customer personas: Detailed profiles of target customers
- Journey stages: Sequential phases of the customer experience
- Touchpoints: All interaction points between customer and brand
- Customer actions: What customers do at each stage
- Emotions: How customers feel throughout the journey
- Pain points: Obstacles and frustrations customers encounter
- Opportunities: Areas for improvement and optimization
Types of Journey Maps:
- Current state maps: Document existing customer experience
- Future state maps: Visualize desired customer experience
- Day-in-the-life maps: Show broader context of customer's day
- Service blueprints: Include behind-the-scenes processes
Benefits of Journey Mapping:
- Identifies gaps in customer experience
- Reveals opportunities for improvement
- Aligns teams around customer needs
- Prioritizes investment in customer experience initiatives
- Facilitates data-driven decision making
Best Practices:
- Base maps on real customer data and research
- Include multiple perspectives from different departments
- Update maps regularly as customer behavior evolves
- Use maps to guide strategic decision making
- Focus on customer emotions, not just actions
Journey mapping serves as a strategic tool that transforms customer insights into actionable business improvements, ensuring that organizations remain customer- centric in their approach to experience design and optimization.










